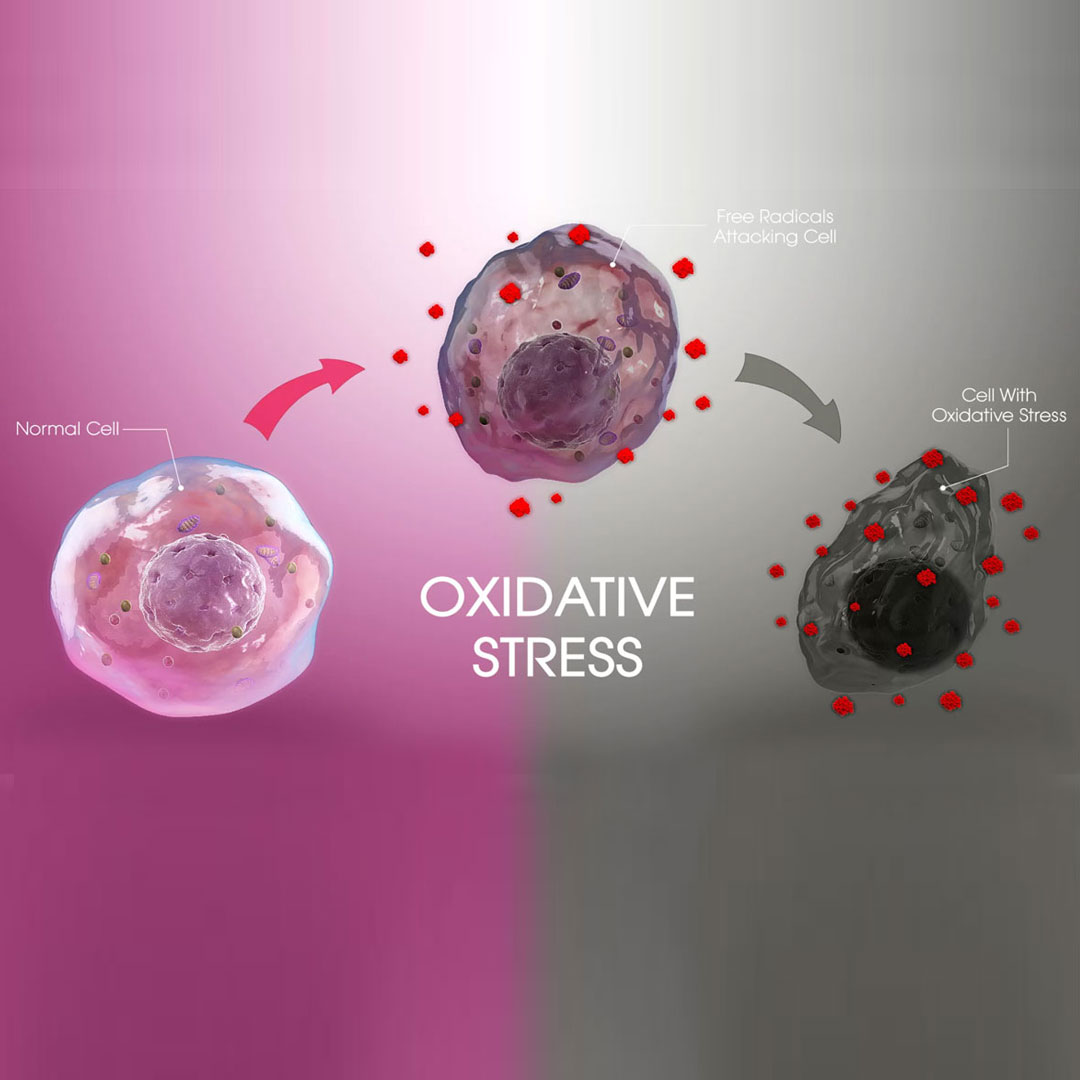
Evaluating oxidative stress in sperm is an essential part of a comprehensive fertility assessment, especially when a couple is experiencing difficulties conceiving.
What is Oxidative Stress in Sperm?
Oxidative stress in sperm occurs due to an imbalance between the production of reactive oxygen species (ROS) and the body's ability to eliminate or neutralize these harmful molecules. When ROS production is excessive or antioxidant defenses are insufficient, oxidative stress can damage sperm quality and function.
Sperm cells are particularly vulnerable to oxidative stress due to their high content of polyunsaturated fatty acids and their lack of protective enzymes found in other cells.
How Oxidative Stress Affects Sperm
- Sperm Damage: ROS can damage sperm membranes, proteins, and DNA, affecting motility (swimming ability) and fertilization potential.
- Reduced Sperm Viability: High oxidative stress levels lower the number of viable sperm.
- Sperm DNA Fragmentation: Oxidative stress can cause breaks or fragmentation in sperm DNA, leading to fertility issues and an increased risk of miscarriage.
Factors Contributing to Increased Oxidative Stress in Sperm
- Lifestyle Factors: Smoking, excessive alcohol consumption, poor diet, and exposure to environmental toxins.
- Infections & Inflammation: Genital infections or inflammation in the reproductive tract can increase ROS production.
- Varicocele: A condition causing enlarged veins in the testicles, associated with oxidative stress.
- Age: Advanced paternal age is linked to increased sperm oxidative stress.
Managing Oxidative Stress in Sperm
- Lifestyle Changes: Improving diet, reducing alcohol and tobacco use, and avoiding environmental pollutants.
- Antioxidant Supplementation: Supplements like Vitamin C, Vitamin E, CoQ10, and zinc may help reduce oxidative stress.
- Medical Treatment: Addressing underlying infections, varicocele, or other conditions affecting sperm health.
- Advanced Sperm Processing Techniques: Methods like microfluidic sperm selection can help isolate sperm with lower oxidative stress for assisted reproduction.
Sperm DNA Fragmentation
The most crucial test for sperm functionality is the DNA fragmentation analysis.
What is Sperm DNA Fragmentation?
Sperm DNA fragmentation refers to the presence of breaks or abnormalities in the DNA strands of sperm cells. The integrity of sperm DNA is critical for successful fertilization and embryo development. High levels of sperm DNA fragmentation are associated with male infertility, failed conception, and increased miscarriage rates.
Causes of DNA Fragmentation in Sperm
- Age (>40 years)
- Unhealthy lifestyle (smoking, alcohol, stress)
- Increased oxidative stress
When is a DNA Fragmentation Test Recommended?
- Low pregnancy success rates despite normal semen analysis
- Poor embryo quality
- Embryo development arrest
- Recurrent miscarriages
- High risk of congenital abnormalities in offspring
Can DNA Fragmentation Be Present Even with a Normal Semen Analysis?
Yes! DNA fragmentation can occur even when standard semen parameters (count, motility, morphology) are normal.
What to Do if Sperm DNA Fragmentation is High?
If DNA fragmentation is above 30%, specialized sperm selection techniques should be used, such as:
- Microfluidic sperm sorting (Microfluidic Chips) – isolates sperm with lower DNA damage.
- ICSI (Intracytoplasmic Sperm Injection) – a precise method of injecting a single high-quality sperm into an egg.
- PICSI (Physiological ICSI) – selects sperm based on their ability to bind to hyaluronic acid, mimicking the natural selection process in the female reproductive system.
Microbiological & Biochemical Testing
Microbiological Testing
Recommended in cases of:
- Previous infections or inflammation
- Unusual semen odor, high viscosity, low motility
It detects:
- Aerobic & anaerobic bacteria
- Ureaplasma, Mycoplasma, Chlamydia
Biochemical Testing
Measures levels of:
- Fructose, Acid Phosphatase, and Alpha-Glucosidase
- Evaluates the function of male reproductive glands (seminal vesicles, prostate, epididymis).
Biochemical testing is crucial for diagnosing azoospermia (absence of sperm) and determining whether it is obstructive or non-obstructive.
Conclusion
Assessing oxidative stress and DNA fragmentation in sperm is essential for diagnosing male fertility issues. If abnormal levels are detected, targeted interventions—including lifestyle changes, medical treatment, and advanced sperm selection techniques—can significantly improve fertility outcomes.