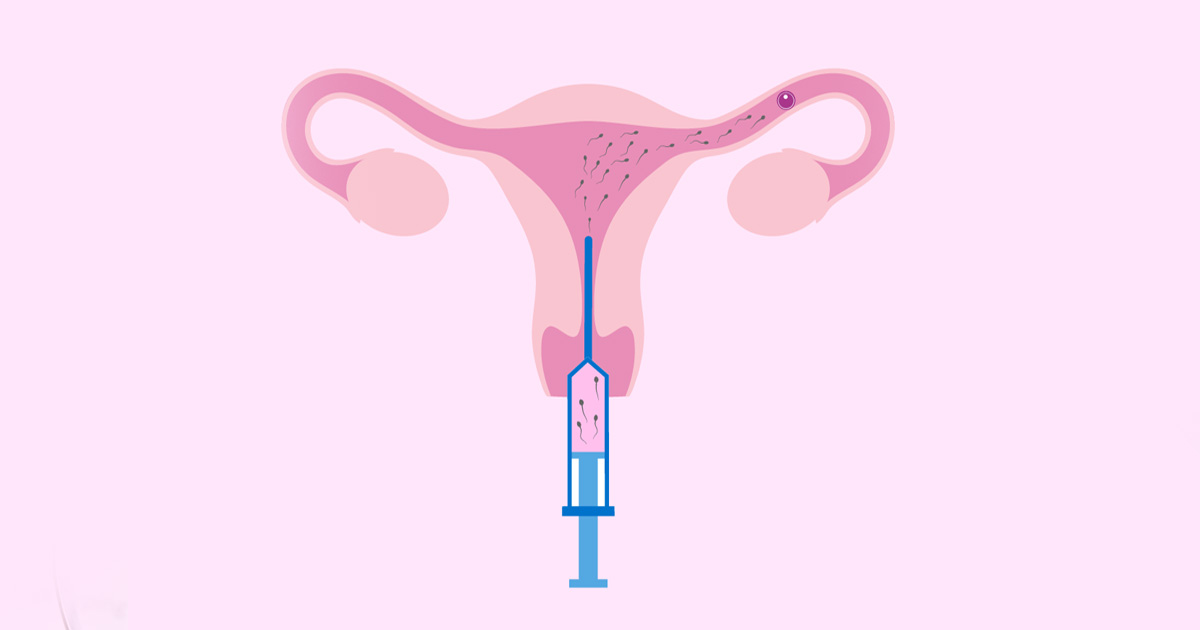
Intrauterine Insemination (IUI) is a fertility treatment where sperm is directly placed inside the woman’s uterus, increasing the chances of fertilization. This method is particularly recommended in cases where no clear cause of infertility has been identified or when minor abnormalities are detected in the sperm analysis.
Steps of the IUI Process:
✔ Ovarian Monitoring or Mild Stimulation:
- The woman may receive medication to stimulate the ovaries and increase the number of eggs produced.
✔ Sperm Collection & Preparation:
- The sperm sample is collected from the partner and processed in the lab to separate the most motile and healthiest sperm for use in the procedure.
- This process is carried out at IASO – Institute of Life.
✔ Sperm Insertion:
- The prepared sperm is inserted directly into the uterus via a thin catheter, aiming to meet the egg and achieve fertilization.
✔ Pregnancy Assessment:
- After the procedure, pregnancy is assessed by monitoring the woman’s cycle and early pregnancy symptoms.
When is IUI Recommended?
IUI is less invasive than IVF and is often considered as a first-line treatment before moving on to more advanced assisted reproductive techniques. It is ideal for women with healthy fallopian tubes and normal ovarian reserves, and is used to treat various fertility issues, such as:
✔ Low sperm count or poor sperm motility
✔ Ejaculatory dysfunction
✔ Inability to have penetrative intercourse
✔ Hostile cervical mucus or cervical scarring
✔ Use of donor sperm
✔ Use of frozen sperm
IUI vs. IVF – Success Rates
- IUI is less invasive and more affordable than IVF, but its success rates are lower.
- The chances of success depend on factors such as:
- The woman’s age
- The cause of infertility
- The use of fertility medications
IUI can be performed on its own or combined with timed intercourse or ovulation induction to maximize the chances of conception.